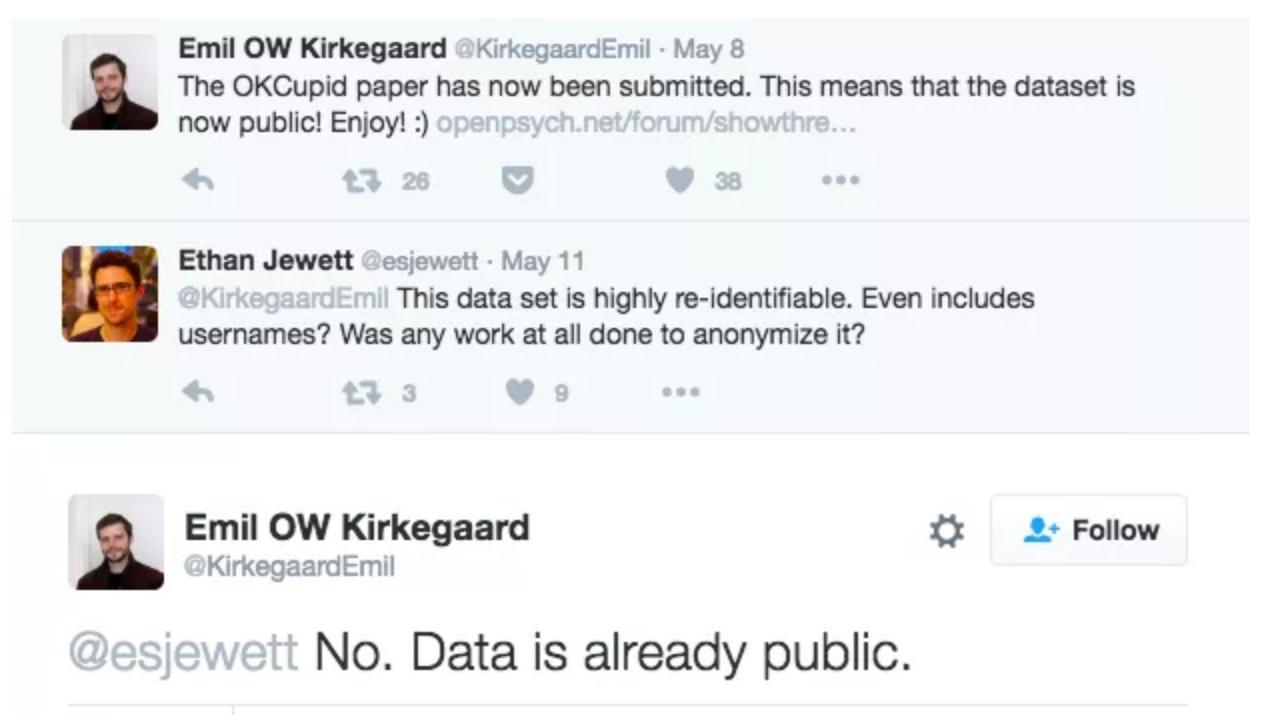
"Can you?" vs "Should you?"
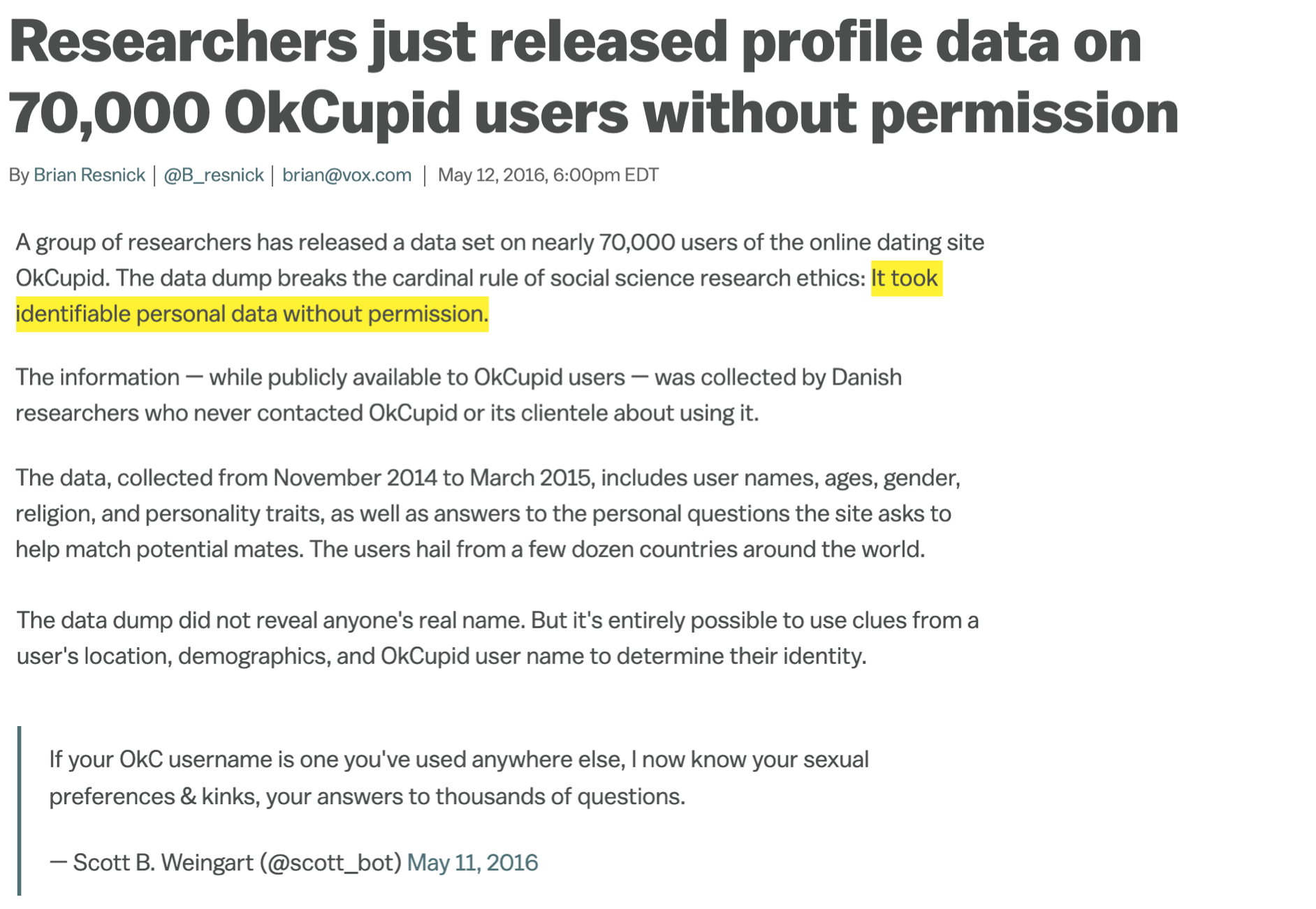
Source: Brian Resnick, Researchers just released profile data on 70,000 OkCupid users without permission, Vox.
3 / 10
Screen scraping vs. APIs
Two different scenarios for web scraping:
Screen scraping: extract data from source code of website, with html parser (easy) or regular expression matching (less easy)
Web APIs (application programming interface): website offers a set of structured http requests that return JSON or XML files
9 / 10
A new R workflow
When working in an R Markdown document, your analysis is re-run each time you knit
If web scraping in an R Markdown document, you'd be re-scraping the data each time you knit, which is undesirable (and not nice)!
An alternative workflow:
- Use an R script to save your code
- Saving interim data scraped using the code in the script as CSV or RDS files
- Use the saved data in your analysis in your R Markdown document
10 / 10